Recording music at home has become increasingly accessible, enabling aspiring musicians and producers to create high-quality tracks without the need for a professional studio. Understanding the essential tools and techniques can transform a simple home setup into a powerful creative space. With the right equipment and knowledge, anyone can start recording their music effectively.
The rise of affordable recording software and technology means that anyone can experiment with their musical ideas from the comfort of their own home. Key components typically include a computer, audio interface, microphone, and digital audio workstation (DAW). With the right combination, individuals can capture their sound and refine it for a polished final product.
Getting started can seem daunting, but with a structured approach, anyone can navigate the basics. Knowledge of sound quality, recording techniques, and editing processes allows for significant improvement over time. This article will guide readers through the necessary steps to successfully record music at home, empowering them to unleash their creativity.
Setting Up Your Home Studio
Creating an effective home studio involves careful consideration of the space, sound quality, and essential equipment. Each element plays a crucial role in achieving high-quality recordings.
Choosing the Right Room
Selecting the appropriate room is fundamental. Ideal spaces are quiet, well-sized, and away from external noise. A room with minimal windows helps reduce sound disturbances.
Consider the following:
- Size: A larger room accommodates better acoustic properties.
- Shape: Irregular shapes help diffuse sound, reducing reflections.
- Location: Avoid areas near busy streets or appliances that create noise.
It’s beneficial to test different rooms. Recording some sound samples and assessing their quality can be enlightening. Choosing the right space can significantly impact the final recording outcome.
Acoustic Treatment
Effective acoustic treatment ensures clarity and quality in recordings. Basic treatment includes minimizing echoes and controlling resonances within the space.
Key acoustic treatments include:
- Bass Traps: Improve low-frequency response by managing bass buildup.
- Acoustic Panels: Absorb mid to high frequencies to reduce reflections.
- Diffusers: Scatter sound waves to maintain a natural sound while preventing echoes.
Placement matters. Bass traps often go in corners, while panels should be positioned at first reflection points. These adjustments lead to a more professional recording environment.
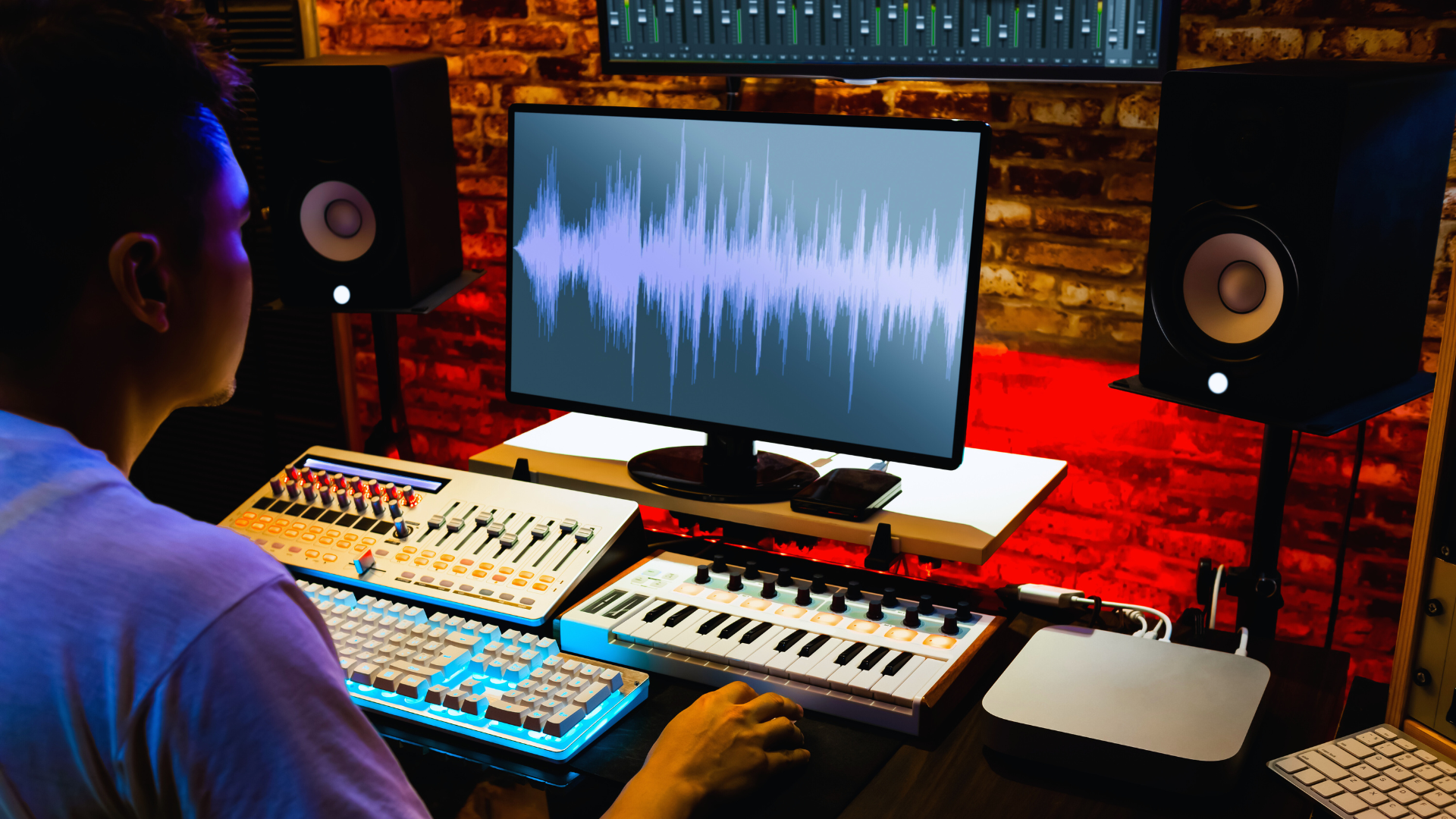
Essential Recording Equipment
Quality recording hinges on the right equipment. Essential items include microphones, audio interfaces, and monitoring speakers.
Basic equipment checklist:
- Microphones: Invest in dynamic or condenser mics suitable for the intended recordings.
- Audio Interface: This device converts analog signals to digital for better sound quality.
- Headphones: Closed-back headphones assist with monitoring without leakage.
- DAW: A Digital Audio Workstation is critical for recording, editing, and mixing.
Overall, it’s important to establish a solid foundation with reliable equipment. Each component must complement the others to achieve top-tier recordings.
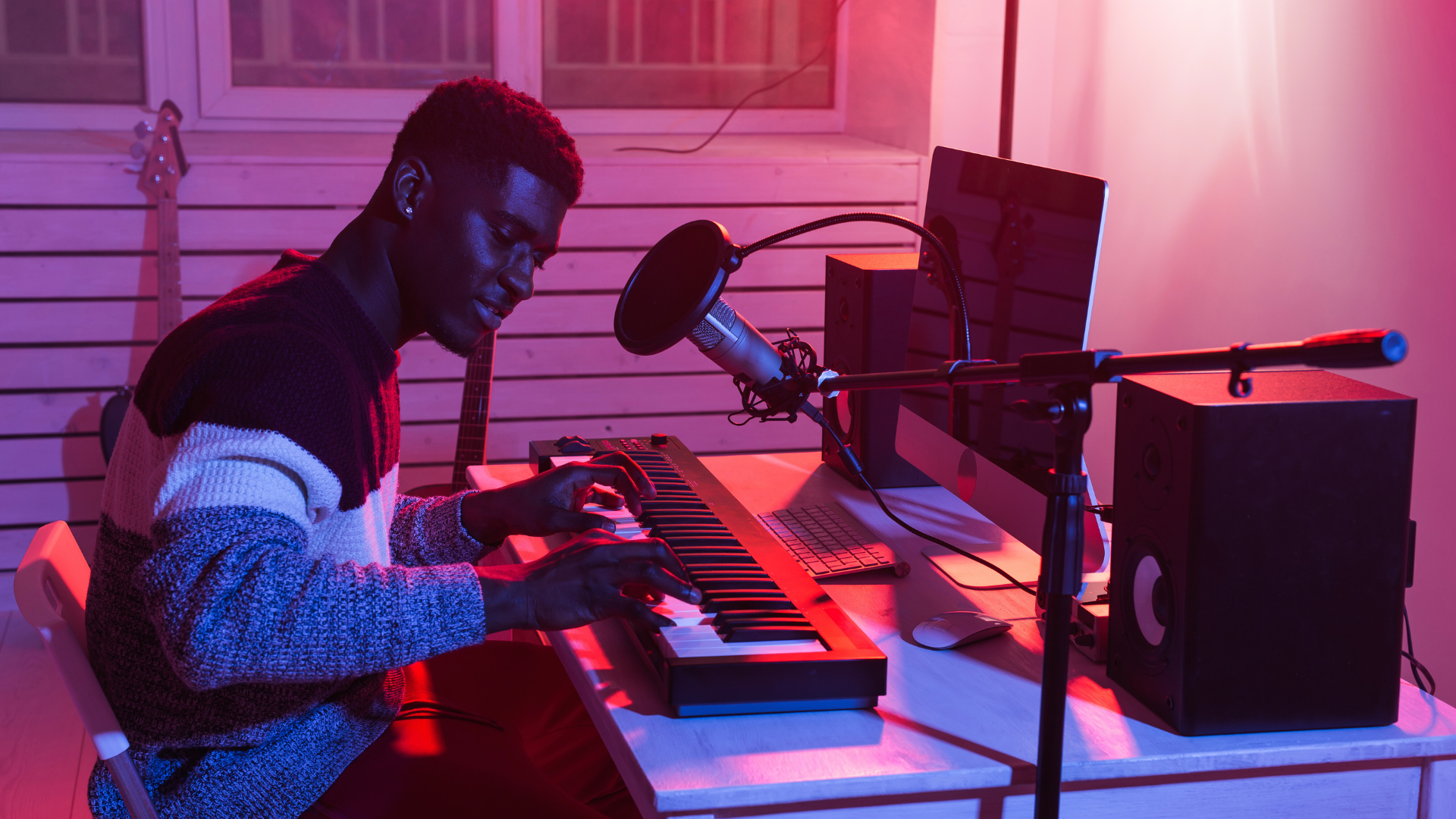
Recording Techniques
Effective recording techniques are crucial for producing high-quality music at home. Attention to microphone placement, signal flow, and levels can significantly impact the final sound.
Microphone Placement
Microphone placement greatly affects the sound quality of a recording. Positioning a microphone too close can result in an exaggerated low end, while placing it too far may lose essential details.
To achieve clear and balanced audio, consider these tips:
- Distance: Start with a distance of 6-12 inches from the sound source.
- Angle: Experiment with angles. For vocals, a slight angle can reduce plosive sounds.
- Room Acoustics: Use dampening materials in the room to minimize unwanted reflections.
Each instrument or voice type may require adjustments, so testing various placements can yield optimal results.
Understanding Signal Flow
Signal flow refers to the path that audio signals take from the source to the recording device. Knowing this flow is essential for troubleshooting and achieving desired sound characteristics.
Key components in signal flow include:
- Sound Source: This could be an instrument, vocal, or any other audio input.
- Microphone: Converts sound waves into electrical signals.
- Interface: Digitizes the audio signals for recording software.
- Software: Recording software captures and processes the sound.
Ensuring that each component is connected properly will help in maintaining sound integrity throughout the recording process.
Achieving Optimal Recording Levels
Setting recording levels is vital to avoid distortion and loss of detail. Too high a level can cause clipping, while too low can introduce noise.
To achieve optimal levels, follow these guidelines:
- Peak Levels: Aim for levels around -12 to -6 dB on the meter to provide headroom.
- Monitor Levels: Use headphones to track sounds in real-time.
- Adjust Inputs: Take time to adjust input gain to find a balance that captures nuances clearly.
Regularly checking levels during the recording session helps ensure a clean final product.
Post-Production Process
The post-production process is crucial for achieving a polished final product. It involves multiple stages, including editing, mixing, and mastering, each adding distinct elements to the music.
Editing
Editing involves fine-tuning the individual tracks recorded during the session. This process includes cutting, duplicating, and adjusting timing for each audio segment.
Key tasks during editing include:
- Removing mistakes: Identify and cut out unwanted noise or errors.
- Tightening performance: Align beats and phrases to improve flow.
- Adding effects: Insert audio effects like reverb or delay to enhance sound.
Tools like Digital Audio Workstations (DAWs) provide features to streamline this process. Understanding how to use these tools effectively can significantly impact the final sound.
Mixing
Mixing is the stage where all the edited tracks come together. It focuses on balancing levels, panning sounds, and incorporating effects.
Consider the following:
- Volume levels: Adjust each track so all elements are heard clearly.
- Panning: Distribute sounds across the stereo field for depth.
- Equalization: Modify frequencies to ensure clarity and prevent muddiness.
Good mixing ensures that individual instruments complement each other without overpowering.
Mastering
Mastering is the final step in the production process. It prepares the mixed track for distribution by ensuring consistency and polish.
Important aspects include:
- Loudness normalization: Adjust the overall volume to meet industry standards.
- Dynamic range control: Use compression to balance softer and louder elements.
- Format preparation: Tailor the final audio for various formats, whether digital or physical.
A well-mastered track sounds cohesive across different playback systems, providing a professional finish to the music.
Releasing Your Music
After creating music, the next crucial steps involve distribution and marketing. This process ensures the music reaches its intended audience effectively.
Distribution Platforms
Choosing the right distribution platform is essential for getting music onto major streaming services. Common platforms include:
- DistroKid: Fast uploads with unlimited songs for an annual fee.
- TuneCore: Offers a pay-per-release model with extensive service options.
- CD Baby: Known for physical distribution and a one-time fee for uploads.
Each platform varies in pricing, features, and revenue splits. Artists should consider their specific needs, such as international reach and reporting capabilities. Understanding the terms and royalties is vital for maximizing earnings.
Marketing and Promotion
Effective marketing strategies can significantly enhance visibility. Social media plays a key role in engaging fans. Here are a few tactics:
- Create a Website: It serves as a central hub for music, merchandise, and updates.
- Utilize Social Media: Platforms like Instagram, Twitter, and TikTok can generate buzz.
- Email Marketing: Build a mailing list to inform fans about releases and events.
Collaborating with influencers and utilizing playlists can further boost reach. Setting a budget for advertising, such as Facebook Ads or Spotify promotions, can also yield beneficial results. Regularly analyzing metrics helps refine strategies for future campaigns.